This map provides an indication of the potential regional impacts of climate change in New Zealand. It is not an attempt to provide a comprehensive summary of all the impacts.
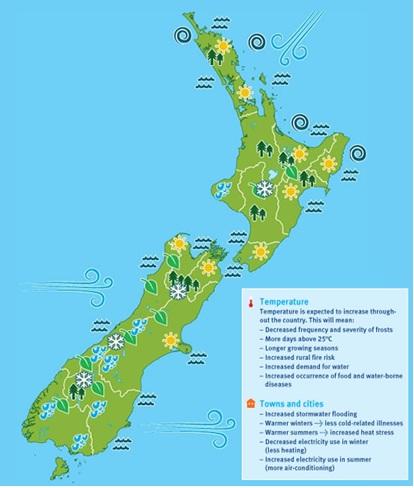
(Source: Ministry for the Environment 2013)
The map above indicates the following effects:
Snowlines and glaciers
- increased length and area of glaciers
- rise in snowline
- possible increase in snowfall
- possible increase in avalanches
Coastal
- sea-level rise
- increased storm surge
- coastal inundation
- increased coastal erosion
Drier northern and eastern parts of North and South Islands
- less rainfall
- decreased run-off to rivers
- increased evaporation
- increased drought for already drought-prone areas
- increased irrigation demand
Wetter west and south of North and South Islands
- increased precipitation
- increased intensity in weather events
- increased flooding for already flood-prone areas
- increased slips
- increased soil erosion
Cyclones
- increased intensity (leading to increased wind, waves, storm surge and rainfall)
Wind
- increased westerly winds in the south, more north easterlies in the north
Natural areas
- species distribution changes
- changes to/loss of habitat
- increased pressure from pests, animals and plants.
Climate change effects by local authority function
|
Local authority area of responsibility |
Asset or activity affected |
Climate change influence |
Possible effects |
|
Water supply and irrigation |
Infrastructure |
Reduced rainfall, extreme rainfall events and increased temperature |
|
|
Wastewater |
Infrastructure |
Increased rainfall |
|
|
Stormwater |
Reticulation |
Increased rainfall |
|
|
Roading |
Road network and associated infrastructure (power, telecommunications, drainage) |
Extreme rainfall events, extreme winds, high temperatures |
|
|
Urban land-use planning/policy development |
Management of development in the private sector |
All |
|
|
Land management |
Rural land management |
Changes in rainfall, wind, and temperature |
|
|
Water management |
Management of watercourses/lakes/ wetlands |
Changes in rainfall and temperature |
|
|
Coastal management |
Infrastructure |
Temperature changes leading to sea-level changes |
|
|
Civil defence and emergency management |
Emergency planning and response, and recovery operations |
Extreme events |
|
|
Biosecurity |
Pest management |
Temperature and rainfall changes |
|
|
Open space and community facilities management |
Planning and management of parks, playing fields and urban open spaces |
Temperature and rainfall changes |
|
|
Transport |
Management of public transport |
Changes in temperatures, wind and rainfall |
|
|
Waste management |
Transfer stations and landfills |
Changes in rainfall and temperature |
|
|
Energy |
Transmission lines |
Extreme wind, high temperatures |
|
